BPMN Activity Types Explained
What are activities in BPMN?
An activity is a generic term for ‘work’ that a company performs in a process. Activities are the critical components of BPMN, since business processes are primarily formed by different types of activities. An activity can be either atomic (a task) or non–atomic, compound (a subprocess). Activities are used in both standard processes and choreographies.


Activities vs subprocesses in BPMN
Activity, the rounded rectangle, represents ‘work’ performed in the process. It is the only flow object that represents work. Activities should be named verb-noun, to indicate the action that they represent. So for example ‘process order’, ‘check inventory’, or ‘send email’. Activities have another unique property: it is the only shape that has a performer. That could either be a person or a system. There are just two types of activities: a task and a subprocess. A task is an atomic activity, meaning it has no internal subparts known to the model. A subprocess is compound, or non-atomic, meaning it does have subparts in the model. It can therefore be expressed as a process. Every activity in BPMN is either a task or a subprocess.
Three BPMN Activity Types
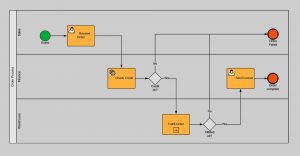
In the level 1 Pallet of BPMN, activities, or tasks, are further specified in three task types. The different task types, are visualized by different icons inside the task shape.

'None' Task Type
The first event type is labeled abstract task type, or ‘none’ task. People often start with modelling ‘none’ task types, and add more detail to the model when the business process advances. From a none task type, you can not tell whether it is a user task or service task.

User Task Type
The second task type is defined as ‘user’. This task type represents any atomic activity carried out by a human. The task differentiates itself with the person symbol inside the rounded rectangle.

Service Task Type
The third task type, is defined as ‘service’ task. The service task type represents any automated atomic activity. Automated means there is no user involved in this process step. Its visualized by a gear symbol inside the task.