Table of Contents
What is BPMN 2.0?
BPMN is a method for mapping out the approach to a business process, it enables to create a visual representation of a complex business practice or process. This helps to understand a process from start to end, and thereby helps to identify the strengths but also the weaknesses of an existing -or to be designed- process.
Through the visual annotation of a process, BPMN enables communication with different stakeholders like project managers, business analysist, managers, subject matter experts and developers, ultimately enabling Business Process Management as a discipline. BPMN is often deployed to make processes more efficient, but it is also a great language to make sure collaboration between different entities run smooth or to make a process compliant with requirements.
What does it stand for?
BPMN stands for Business Process Modeling Notation. It’s a graphical notation style, or a visual language that enables the description and optimization of business processes. BPMN is a standard that is created and maintained by The Open Management Group: OMG. Since BPMN is a standard, it’is vendor-neutral and the precise meaning of the graphical elements and relationships are defined in a specification.
Diagrams that you create using BPMN 2.0, are very valuable: they enable communication between different teams, business units, and organizations, even if they use a different tool. Ultimately this type of modeling, enables analysis and improvement of a broad range of business processes, organization wide. But what does BPMN 2.0 look like?
What is a Business Process Modelling Notation diagram?
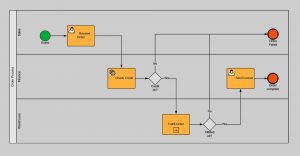
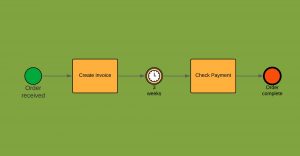
A simple business process modeling notation diagram looks like this:

The basics of the BPMN notation are very simple. There are just three primary shapes of flow objects: activity, gateway, and event. The solid arrow, called a sequence flow, can only connect to a flow object. BPMN is a flowchart-based modelling language. It describes processes as a flow of activities or actions, arranged in swimming lanes and pools, representing activity performers. The advantage of using swimming lanes is that the visual language enables the communication of a logic process where all actors in a process are included in the diagram. As discussed, BPMN is thus a flowchart-based diagramming style. But there are also four important differences between the business process modeling notation and ‘normal’ flowchart diagramming.
The differences between flowcharting and BPMN
First, since BPMN is a standard, the meaning of the shapes in the diagram are precisely defined in the specification. This contributes to the general usability of the language, as professionals from different teams or organizations understand the models without further explanation. As a result, BPMN creates, as it were, a common language.
Second, the BPMN language is hierarchical: the hierarchical diagram structure does not put all process steps in a flat single level model that is hard to understand, but it enables you to collapse big chunks of the process into single activities called subprocesses. Those subprocesses can be arranged in a top level process diagram that shows the essential high-level features of the process in a glance: how it starts, its possible end-states and what the instances represent. The details of each sub-process are expressed as mini processes and can be expanded if needed.
Third, BPMN allows you to model interactions with external entities, such as a customer, a service provider, a technology partner or other entity. This enables integral modelling of the full business context. This is important as actual processes often depend on external partners. In order to improve such processes, it must be fully transparent which entities are involved.
Fourth, BPMN differs from traditional flowcharts by putting event triggered behavior inside the diagram, where traditional flowcharts usually leave the start of the actual process outside the scope of the model. An event should be seen as a signal that something happened. The signal is then considered the event trigger. The inclusion of events in BPMN are important, since they are an important process behavior in the real world. Exceptions happen, and processes have to respond to those exceptions. BPMN enables you to describe that response inside the diagram itself, ultimately enabling you to improve real world processes.
What is the purpose of the Business Process Modelling Notation?
In this article we already discussed several reasons why BPMN is important and how it will help you to improve real world processes. A short summary about the key benefits of the Business Process Model Notation:
- It’s a standard, it is vendor neutral and widely deployable.
- It provides a common process description language, enabling shared understanding across the enterprise. Between business people and IT people andbetween business units and organizations.
- It enables BPM as management discipline: it helps understanding end to end processes as a single thing, as opposed to multiple things.
- It includes events inside the diagram, herewith representing real world processes . By putting event handling in the annotation, the business is now empowered to model what does happen or what should happen when these instances occur.
By adopting BPMN you will be able to describe, analyse and improve real world business processes. Interested in learning more about BPMN? Follow our free introduction to BPMN training over here!